Encryption > Glossary > Ciphertext
What is ciphertext? A complete guide
Ciphertext keeps your messages, passwords, payments, and personal data safe online. Secure apps use encryption to turn your information into ciphertext, protecting it from hackers and snoopers.
Learn how ciphertext works and why choosing the right apps makes a difference.

What is ciphertext?
Ciphertext is the encrypted form of readable information, called plaintext. When data such as a message, password, or file is encrypted using a mathematical algorithm and a key, it becomes scrambled into ciphertext. This encrypted text looks random or meaningless to anyone who does not have the correct key, which helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
How does ciphertext work?
Ciphertext is created through a process called encryption, where plaintext is passed through a cipher (an encryption algorithm) along with a secret key. The algorithm rearranges or transforms the data into an unreadable format. To recover the original information, decryption is performed using the correct key.
In symmetric encryption, the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption uses two keys: a public key to encrypt the data and a private key to decrypt it. Even if encrypted data is intercepted, it cannot be understood without the proper key.
Historically, encryption was done by hand using simple methods like replacing letters (substitution ciphers) or rearranging them (transposition ciphers) — now outdated because they are easy to break. Modern encryption algorithms such as AES-256 and ChaCha20 use long, complex keys to secure data, making ciphertext extremely difficult to break using brute-force attacks.
A simple example of how ciphertext works
When you use a secure messaging app to text a friend “Meet me at 8 PM,” the app encrypts the message before it leaves your phone, turning it into ciphertext. When it arrives on your friend’s device, their app uses the correct encryption key to convert the ciphertext back into the original message.
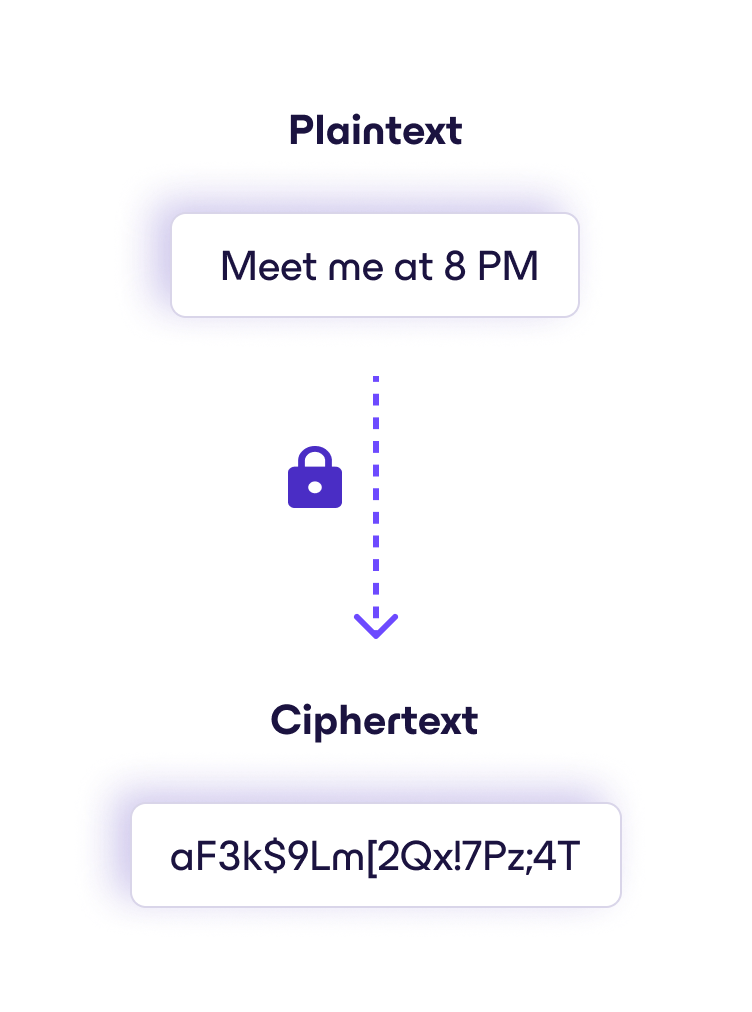
If anyone intercepts the message along the way — whether a hacker, a network provider, or even the app company itself (if the service uses end-to-end encryption) — they would only see scrambled data. Without the private encryption key stored on your friend’s device, the message remains unreadable.
Proton Mail ciphertext
Proton Mail uses end-to-end encryption to protect your messages. While your emails appear readable when you send and receive them, that’s because your device has the correct encryption keys to convert the ciphertext back into plaintext. If anyone attempted to intercept your messages in transit — including Proton itself — they wouldn’t see the actual contents of your email, only encrypted ciphertext like the example below.
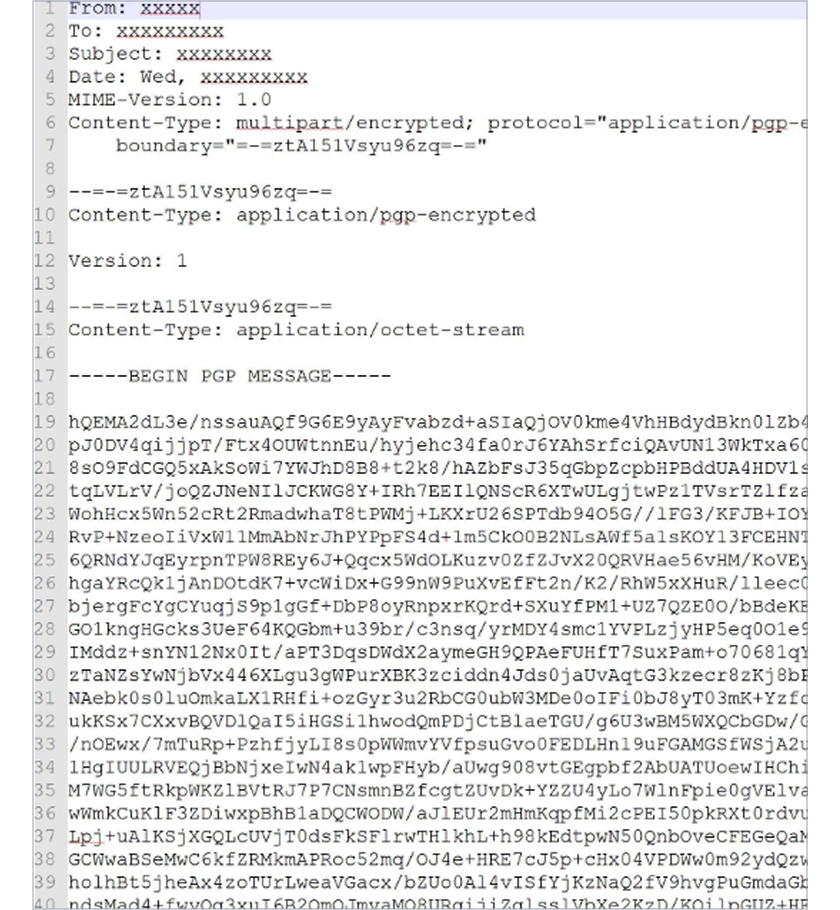
This ciphertext is significantly more complex, and can only be deciphered using the correct encryption key.
Historical examples of ciphertext
Encryption and ciphertext has been around for thousands of years and has taken many different forms. Here are some famous examples of ciphers and ciphertext:
Caesar cipher
The Caesar cipher is one of the simplest and oldest encryption methods. It works by shifting each letter in a message a fixed number of places down the alphabet to produce ciphertext. This kind of encryption method, where each letter is replaced with another according to a rule or key, is known as a substitution cipher — the Caesar cipher is just one example of this type.
An example of ciphertext created with a Caesar cipher is JV PBZOBQ QBUQ. In this case, each letter of the original message was shifted three letters backward in the alphabet to hide the meaning:
- A becomes X
- B becomes Y
- C becomes Z
- and so on.
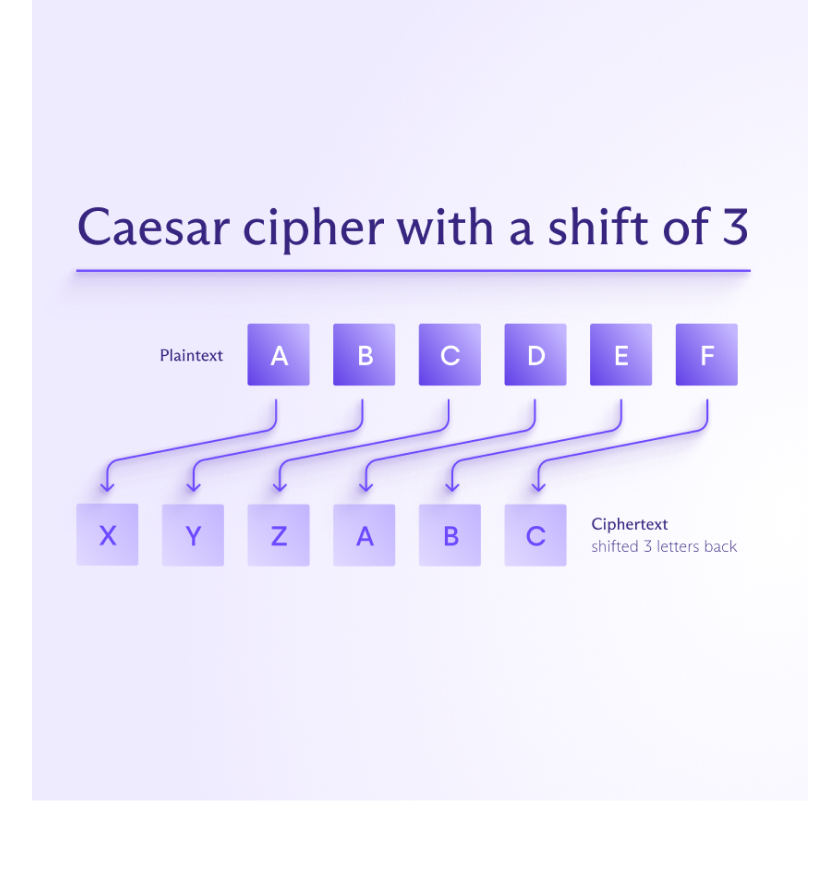
To decrypt this message, you simply shift each letter three places forward in the alphabet, so the cipher key is 3.
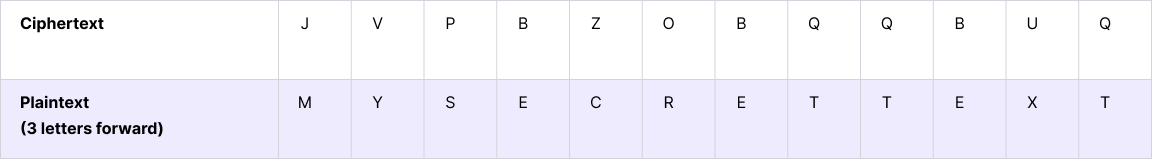
Decrypting the message produces the plaintext MY SECRET TEXT.
Voynich manuscript

The Voynich manuscript is one of the most famous unsolved texts in the world. Dating to the early 15th century, it is written in an unknown script and filled with unusual illustrations of plants, astronomical diagrams, zodiac symbols, and mysterious figures.
Many researchers believe the manuscript could be encrypted text, possibly a sophisticated cipher from the medieval period. Others argue it might represent an invented or lost language, or an elaborate hoax.
The Zimmermann telegram

The Zimmermann telegram was a secret diplomatic message sent from the German Foreign Office to the Mexican government in 1917 during World War I. It proposed a military alliance between Germany and Mexico if the United States entered the war against Germany.
British intelligence decoded the telegram using intercepted messages and German code material they had earlier captured.
Zodiac letters
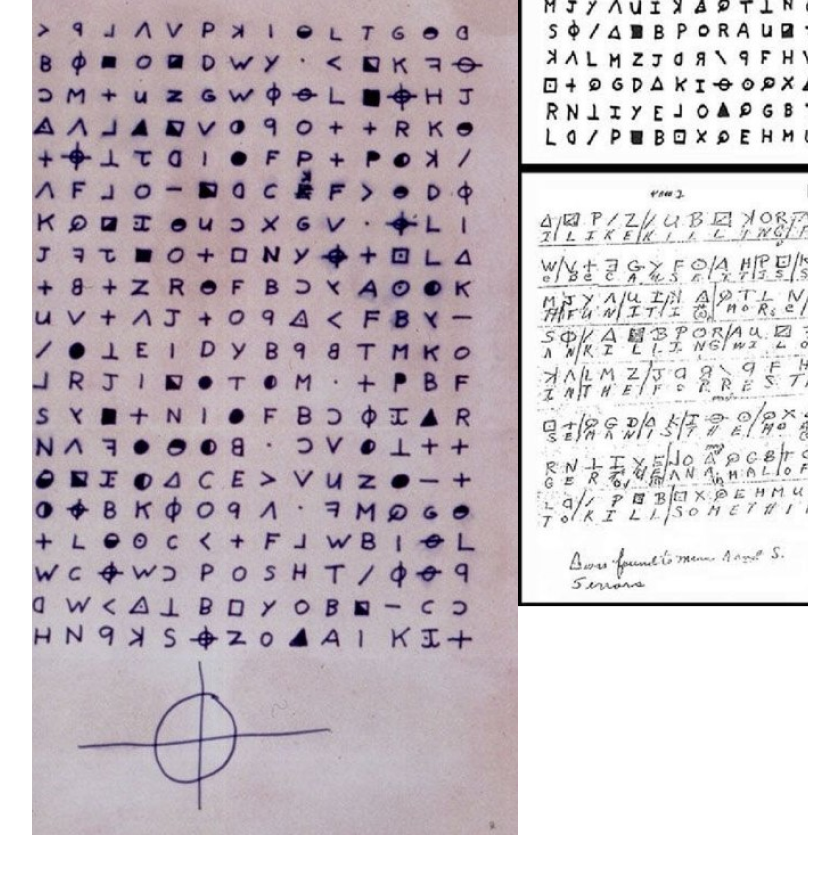
The Zodiac letters are a series of messages sent to newspapers in the late 1960s and early 1970s by the unidentified Zodiac Killer, a serial killer who operated in Northern California. The first cipher was solved by amateur codebreakers, and another one remained unsolved for over 50 years before being cracked in 2020 using modern cryptanalysis tools. Some shorter ciphers are still unsolved today.
Why ciphertext matters today
Ciphertext is the result of encryption, and encryption underpins much of modern digital life, helping to protect personal data, financial activity, and communications. Individuals benefit from safer online interactions, while governments and businesses depend on encryption to safeguard sensitive systems and information.
Here are some everyday ways in which ciphertext shows up, often invisibly:
- Secure websites (HTTPS): When you log in, shop, or fill out forms online, your browser encrypts the data before sending it.
- Messaging apps: Secure chat services like Signal encrypt messages so only the intended participants can read them.
- Online banking and payments: Encryption protects account credentials, card details, and transaction data.
- Cloud storage and backups: Files are frequently encrypted to remain protected. If the cloud storage uses end-to-end encryption, not even the provider can access your data.
- Device encryption: Most phones and laptops can use full-disk encryption to turn stored data into ciphertext so that if the device is lost or stolen, the information on it remains inaccessible without the proper credentials.
Frequently asked questions
- How is ciphertext created?
- Can you decrypt ciphertext without a key?
- Is ciphertext the same as encoding or hashing?
- Which ciphers produce ciphertext today?
Take charge of your data
Proton was built to protect your data from the start. With end-to-end encryption, open-source apps, and independent audits, your information stays yours.